
Michael Shoory, Senior Economist
Michael is currently conducting economic impact analysis and custom research projects.
Travel and Tourism | Europe
Developments surrounding the outbreak of COVID-19 continue to change at a rapid pace, as does the expected impact on tourism. The outlook for global travel has deteriorated further in the past two weeks (when Tourism Economics’ previous research briefing was published) and Europe has become the new epicentre of the virus. Movement into, out of, and within Europe has been significantly restricted, and in an unprecedented development most countries within the Schengen zone have reintroduced border controls.
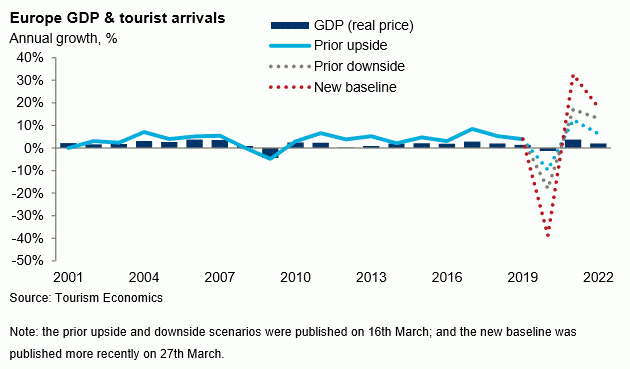
Our new baseline projection is for a reduction in global arrivals of 39% in 2020 compared with last year – more than double the fall in the downside projection from mid March. The projected fall in arrivals to Europe is in line with the global decline, and is equivalent to 287 million fewer international visitors than in 2019. By country, Italy is the most affected in percentage terms (a decline of 49%), followed by Spain (-42%), though France is projected to suffer the largest decline in volumes (38 million fewer arrivals). A rapid recovery is expected in 2021, but the 2019 volumes of international arrivals are not expected to be regained until 2023. The full details of these forecasts, and an estimate for the impact on domestic travel, are in Tourism Economics’ new research brief, Updated Coronavirus Impacts on European Tourism; forecasts have also been published in the Global Travel Service database.

Michael Shoory, Senior Economist
Michael is currently conducting economic impact analysis and custom research projects.
Unsurprisingly, we consider there to be significant uncertainty surrounding these forecasts and the path to recovery. Our upside scenario – in which current travel restrictions are eased before the peak summer tourism period – sees a smaller decline of 28% in international arrivals to Europe. By contrast, the downside path involves 18 months of impacts, and a much more significant fall in tourism.